Vitamins C and D have become household names in modern nutrition, and for good reason. These essential nutrients play critical roles in keeping our bodies functioning at their best. Vitamin D helps regulate calcium absorption and supports bone health, while vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant and supports collagen production. Both vitamins are vital for a strong immune system, which explains why they’ve captured so much attention in recent years.
Many people assume they can get all the vitamin D they need from food sources like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified dairy products. While these foods certainly contribute to your daily intake, relying solely on vitamin D-rich foods often falls short of meeting optimal health requirements. The reality is that very few foods naturally contain significant amounts of vitamin D. A 3-ounce serving of salmon provides about 450 IU of vitamin D, but the recommended daily allowance ranges from 600 to 800 IU for most adults, and some individuals may need even more depending on their age, location, and sun exposure.

The challenge becomes even more complex when we consider that vitamin D works best when paired with other nutrients. This is where the science of combining vitamins C and D in modern supplements becomes particularly compelling. Rather than treating these vitamins as isolated nutrients, forward-thinking supplement manufacturers are recognizing the value of addressing multiple nutritional needs simultaneously through thoughtful formulation strategies.
The Complementary Partnership of Vitamins C and D
The relationship between vitamins C and D goes beyond simple coexistence in a supplement bottle. These nutrients work together in ways that enhance each other’s effectiveness, particularly when it comes to immune function and skeletal health.
Vitamin D is well known for its role in calcium absorption and bone mineralization. It helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the bloodstream, ensuring that bones receive the minerals they need to stay strong. However, vitamin D doesn’t work alone in maintaining skeletal health. Vitamin C plays an equally important role by supporting collagen synthesis, the structural protein that forms the framework upon which minerals are deposited in bones. Studies show that the bioavailability of vitamin C is relatively good, with 70-90% being absorbed with dietary intakes below 1,000 mg. This high absorption rate makes it an ideal partner for vitamin D in bone health formulations.
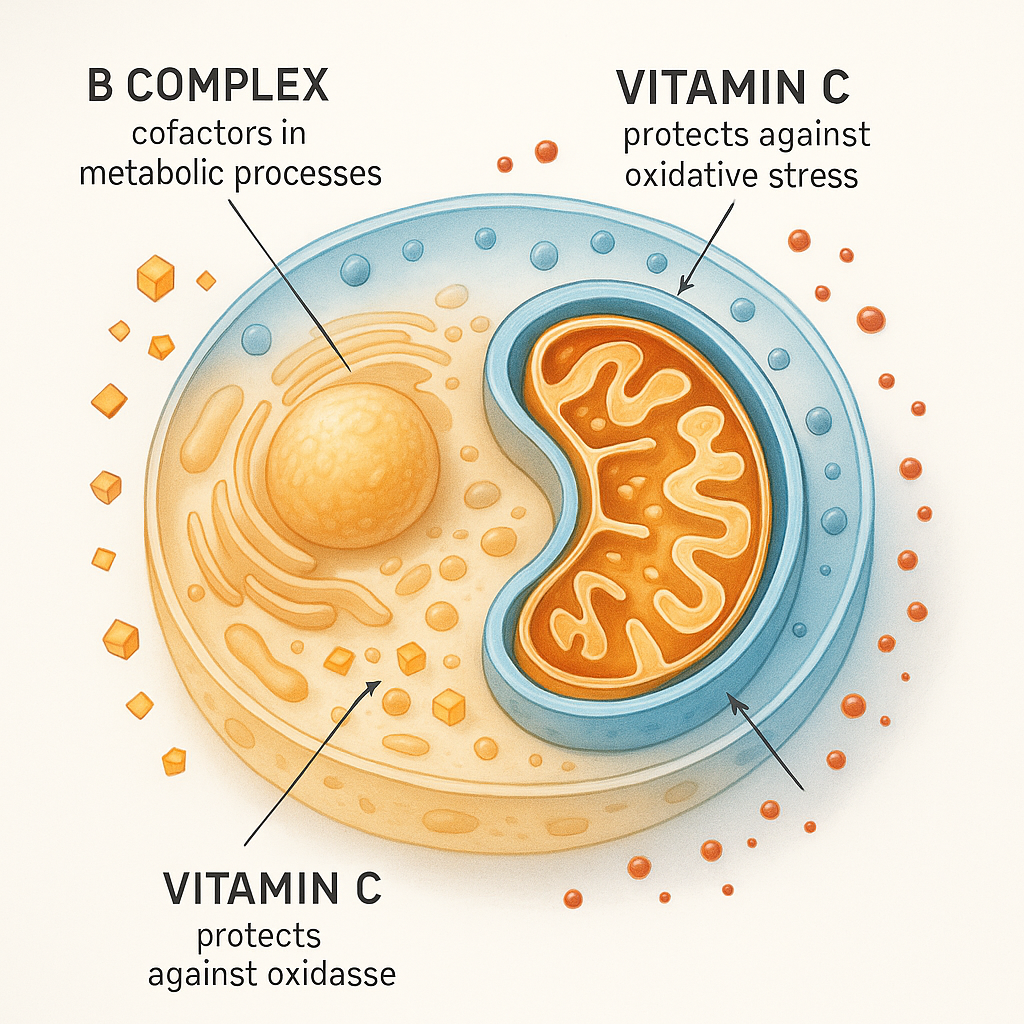
When it comes to immune function, both vitamins contribute to the regulation of immune responses through different mechanisms. Vitamin D modulates the innate and adaptive immune systems, helping the body respond appropriately to threats. Vitamin C supports various cellular functions of both the innate and adaptive immune systems, while also acting as an antioxidant that protects immune cells from oxidative stress during infection. By taking vitamin C and D together, we may enhance our body’s ability to mount effective immune responses while minimizing cellular damage.
From a practical standpoint, combining these vitamins in supplements addresses multiple nutrient needs efficiently. Many individuals struggle to get adequate amounts of both vitamins from food alone. While citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens provide vitamin C, and fatty fish and fortified foods offer vitamin D, consuming enough of these foods daily requires careful meal planning that many people find difficult to maintain. A well-formulated supplement can fill these nutritional gaps without requiring consumers to take multiple separate products throughout the day.
The synergistic benefits of combining vitamins C and D extend to wound healing as well. Vitamin C is essential for collagen formation during the healing process, while vitamin D helps regulate inflammatory responses and promotes tissue repair. This combined action supports faster and more complete wound healing, particularly important for individuals recovering from surgery or managing chronic wounds.
Formulation and Stability Considerations
Creating an effective vitamin C and D combination supplement presents unique technical challenges that require sophisticated formulation strategies. Understanding these challenges is crucial for supplement manufacturers who want to deliver products that maintain potency from production through consumption.
Vitamin C presents one of the most significant stability challenges in supplement formulation. As a water-soluble vitamin, ascorbic acid is highly sensitive to heat, light, oxygen, and moisture. When exposed to these elements, vitamin C can degrade rapidly, reducing the potency of the supplement over time. This sensitivity means that manufacturers must implement protective measures during both production and packaging.
Several strategies have proven effective in addressing vitamin C’s stability issues. Encapsulation technologies, such as liposomal delivery systems, have shown promising results. Nine studies demonstrated that liposomal vitamin C had higher bioavailability than non-liposomal forms, with 1.2-5.4-fold higher maximum concentration levels and 1.3-7.2-fold higher area under the curve measurements. These advanced delivery systems not only protect vitamin C from degradation but also enhance its absorption in the body.

Vitamin D, being fat-soluble, presents a different set of formulation considerations. While generally more stable than vitamin C, vitamin D still requires careful attention to ensure optimal bioavailability. The choice between vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) matters, though current research considers both forms bioequivalent in most applications. Many formulators prefer vitamin D3 because it’s the form naturally produced in human skin when exposed to sunlight.
The challenge in combining these two vitamins lies in creating a formulation that protects the sensitive vitamin C while ensuring the fat-soluble vitamin D is properly delivered for absorption. At NutraAeon, we understand that premium-quality ingredients require equally sophisticated delivery systems. Our comprehensive supply network provides access to stabilized vitamin C forms and highly bioavailable vitamin D3 that meet the demanding needs of today’s health-conscious consumers.
Hygroscopic ingredients present some of the most challenging formulation problems in capsule manufacturing. When combining water-soluble and fat-soluble vitamins, manufacturers must carefully select excipients that protect against moisture absorption while maintaining product stability. The packaging itself becomes a critical component, with moisture barriers and light-protective materials essential for maintaining potency throughout the product’s shelf life.
Bioavailability, Absorption, and Dosage Guidelines
Understanding how vitamins C and D are absorbed in the body reveals why certain formulations work better than others and helps establish appropriate dosage guidelines for consumers and manufacturers alike.
Vitamin C and vitamin D function through different absorption mechanisms—vitamin C is water-soluble while vitamin D is fat-soluble—meaning they do not interfere with one another during absorption. This independence makes them ideal candidates for combination supplements. Vitamin C is absorbed primarily in the small intestine through sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters. One hundred percent absorption efficiency is observed when ingesting vitamin C at doses up to 200 mg at a time, but higher doses (>500 mg) result in fractionally less absorption as the transporters become saturated.
This absorption characteristic has important implications for formulation. Rather than providing mega-doses of vitamin C in a single tablet, sustained-release formulations or multiple smaller doses throughout the day can maximize absorption and maintain consistent blood levels. Clinical data indicate that between 80 and 100% of vitamin C at single doses up to 100-200 mg are fully absorbed into the bloodstream, highlighting the importance of appropriate dosing strategies.
Vitamin D absorption follows a different pathway. As a fat-soluble vitamin, it requires dietary fats for optimal absorption. This is why many vitamin D supplements are formulated with oils or recommend taking the supplement with meals containing fat. The bioavailability of vitamin D can be significantly enhanced through careful formulation choices, including the use of specific carrier oils and emulsification techniques that improve its solubility and absorption.
Pairing certain nutrients, such as vitamin C with iron or vitamin D with calcium, can further enhance bioavailability and optimize health benefits. This principle of nutritional synergy informs modern supplement design, where the goal extends beyond simply delivering individual nutrients to creating formulations that maximize their collective impact.
Dosage guidelines for vitamins C and D must balance efficacy with safety. For vitamin C, the recommended daily allowance is 75-90 mg for adults, though many supplements provide higher amounts (500-1000 mg) based on research suggesting potential benefits at these levels. Upper limits are set at 2000 mg per day, beyond which some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort. For vitamin D, the recommended daily allowance ranges from 600-800 IU for most adults, with upper limits set at 4000 IU per day. However, individual needs vary based on factors like sun exposure, skin pigmentation, age, and geographic location.
Safety considerations also require attention to individual circumstances. People taking certain medications, those with specific health conditions, or individuals already consuming fortified foods should consult healthcare professionals before starting supplementation. Generally, taking vitamin C and D together does not pose significant risks and is considered safe when following recommended guidelines.
Regulatory Standards and Quality Control
The supplement industry operates within a complex regulatory framework designed to protect consumers while allowing innovation. For manufacturers sourcing nutritional ingredients, understanding these requirements and maintaining rigorous quality standards isn’t optional—it’s fundamental to building trust and delivering products that truly serve consumer health.
Regulatory and labeling requirements for supplement manufacturers stress the necessity for transparency and quality control at every stage of production. In the United States, the FDA regulates dietary supplements under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA), which requires accurate labeling, good manufacturing practices (cGMP), and substantiation of claims. Manufacturers must ensure that their products contain what the label claims and are free from contaminants.
This regulatory landscape creates both opportunities and challenges for dietary supplement manufacturers. Companies that embrace these standards as minimum baselines rather than maximum targets position themselves as industry leaders. Complete documentation, certificates of analysis, and full supply chain visibility from source to delivery have become essential components of responsible manufacturing.
Quality control extends beyond regulatory compliance to encompass industry-leading testing protocols and rigorous verification of every ingredient. For vitamins C and D specifically, this means testing for potency, purity, and stability throughout the product lifecycle. Heavy metal testing, microbial analysis, and verification of vitamin content ensure that products deliver on their promises from production through the end of shelf life.
At NutraAeon, we believe in delivering excellence through every aspect of our service, with quality, transparency, and empowerment forming the foundation of our approach. Our industry-leading testing protocols exceed USP and FDA expectations, providing manufacturers with the confidence that comes from working with premium-quality ingredients. We specialize in comprehensive vitamin offerings, including multiple forms of vitamin C, vitamin C palmitate, and vitamin E tocopherols, sourced through our global supply network and verified through rigorous quality control measures.
The importance of supply chain transparency cannot be overstated. Consumers increasingly want to know not just what’s in their supplements but where ingredients come from and how they’re processed. Manufacturers who can provide this level of transparency, backed by thorough documentation and third-party testing, build lasting trust with their customers.
Labeling accuracy represents another critical aspect of regulatory compliance. Labels must accurately reflect vitamin content, using internationally recognized units (IU for vitamin D, mg for vitamin C) and providing clear guidance on serving sizes and daily value percentages. Any claims about health benefits must be carefully worded to comply with regulatory requirements while still communicating value to consumers.
Making Informed Choices About Supplementation
For consumers navigating the crowded supplement marketplace, understanding how to prioritize food sources while using supplements wisely to fill nutritional gaps represents essential knowledge for optimizing health outcomes.
Food should always be the first line of defense in meeting nutritional needs. Whole foods provide not just individual vitamins but a complex matrix of nutrients, fiber, and phytochemicals that work together in ways we’re still discovering. For vitamin C, excellent food sources include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts. These foods provide vitamin C alongside other beneficial compounds that enhance its absorption and effectiveness.
For vitamin D, the challenge is greater. Very few foods naturally contain significant amounts of this crucial vitamin. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines provide good amounts, as do egg yolks and fortified dairy products. However, even a varied diet often falls short of optimal vitamin D intake, particularly for people living in northern latitudes, those with darker skin, or individuals who spend limited time outdoors.
This is where supplements become valuable tools rather than replacements for healthy eating. A well-formulated vitamin C and D supplement can efficiently fill nutritional gaps that diet alone cannot address. The key is choosing products that demonstrate quality and transparency through their formulation, testing, and labeling practices.
When evaluating supplement products, consumers should check product credentials carefully. Look for products that provide certificates of analysis, list all ingredients clearly, and use forms of vitamins known for high bioavailability. Third-party testing certifications from organizations like NSF International or USP provide additional assurance of quality and accuracy. The manufacturer’s reputation matters too—companies committed to transparency and quality control are more likely to deliver products that meet their label claims.
Consulting healthcare professionals when necessary provides personalized guidance that generic recommendations cannot match, especially when determining appropriate dosages for specific populations. Healthcare providers can assess individual risk factors, test vitamin D levels, and recommend appropriate supplementation strategies based on specific health status, medications, and lifestyle factors. This personalized approach ensures that supplementation supports rather than potentially complicates individual health situations.
The decision to supplement should also consider timing and consistency. Both vitamins C and D benefit from regular, consistent intake rather than sporadic mega-dosing. Vitamin C, being water-soluble, isn’t stored long-term in the body, making daily intake important for maintaining optimal levels. Vitamin D, while fat-soluble and stored in body tissues, still requires regular supplementation for those not getting adequate sun exposure or dietary sources.
Understanding the science behind pairing vitamins C and D in modern supplements empowers both consumers and manufacturers to make informed decisions. For manufacturers, this knowledge drives formulation strategies that maximize bioavailability, stability, and efficacy. For consumers, it provides the foundation for choosing supplements that truly support their health goals while maintaining realistic expectations about what supplementation can and cannot achieve.
The future of nutritional supplementation lies in this intersection of scientific understanding, quality manufacturing, and consumer education. As research continues to reveal the complex interactions between nutrients and their roles in human health, the importance of thoughtful formulation and responsible sourcing becomes ever more apparent. Companies like NutraAeon, committed to providing premium-quality ingredients and comprehensive support to manufacturers, play a crucial role in elevating industry standards and empowering formulations that genuinely serve consumer health.
Ultimately, the goal is simple: helping people achieve optimal health through science-backed nutrition, whether from food, supplements, or the thoughtful combination of both. By understanding why vitamin D foods alone fall short and how modern supplements can effectively pair vitamins C and D, we take another step toward that goal.