When you bite into a fresh orange or slice open a bell pepper, you’re not just getting vitamin C. You’re experiencing nature’s complete nutritional package—a sophisticated blend of ascorbic acid, bioflavonoids, fiber, and dozens of complementary compounds working in concert. Yet most supplement manufacturers miss this critical insight entirely, focusing solely on synthetic ascorbic acid while ignoring the cofactors that make natural vitamin C foods so remarkably effective.
This manufacturing secret isn’t just about marketing natural versus synthetic. It’s about understanding why whole food sources consistently demonstrate superior outcomes in clinical applications, and how forward-thinking manufacturers can bridge this gap. The difference lies in bioavailability, stability, and the synergistic relationships that make vitamin C absorption far more complex than simply delivering isolated ascorbic acid to consumers.
For supplement manufacturers navigating today’s clean-label revolution, this distinction matters more than ever. Consumers increasingly demand products that mirror the nutritional intelligence of whole foods, creating both challenges and opportunities for brands willing to innovate beyond conventional approaches.
The Science Behind Vitamin C Absorption: Why Natural Sources Perform Differently
The human body absorbs vitamin C through a tightly regulated mechanism that most manufacturers fundamentally misunderstand. When you consume vitamin C, whether from citrus fruits or supplements, your intestinal cells transport it using specialized sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters. These biological gatekeepers don’t simply accept unlimited quantities—they regulate absorption based on plasma concentration, creating a ceiling effect that many high-dose supplements fail to acknowledge.
Research demonstrates that at moderate doses around 100-200mg, the body absorbs approximately 80-90% of consumed vitamin C. However, as dosage increases beyond 1,000mg, absorption rates plummet dramatically to below 50%. This isn’t a manufacturing defect—it’s biological design. Your body maintains homeostatic control over vitamin C levels, actively limiting absorption when tissues are saturated and increasing excretion of excess amounts through urine.
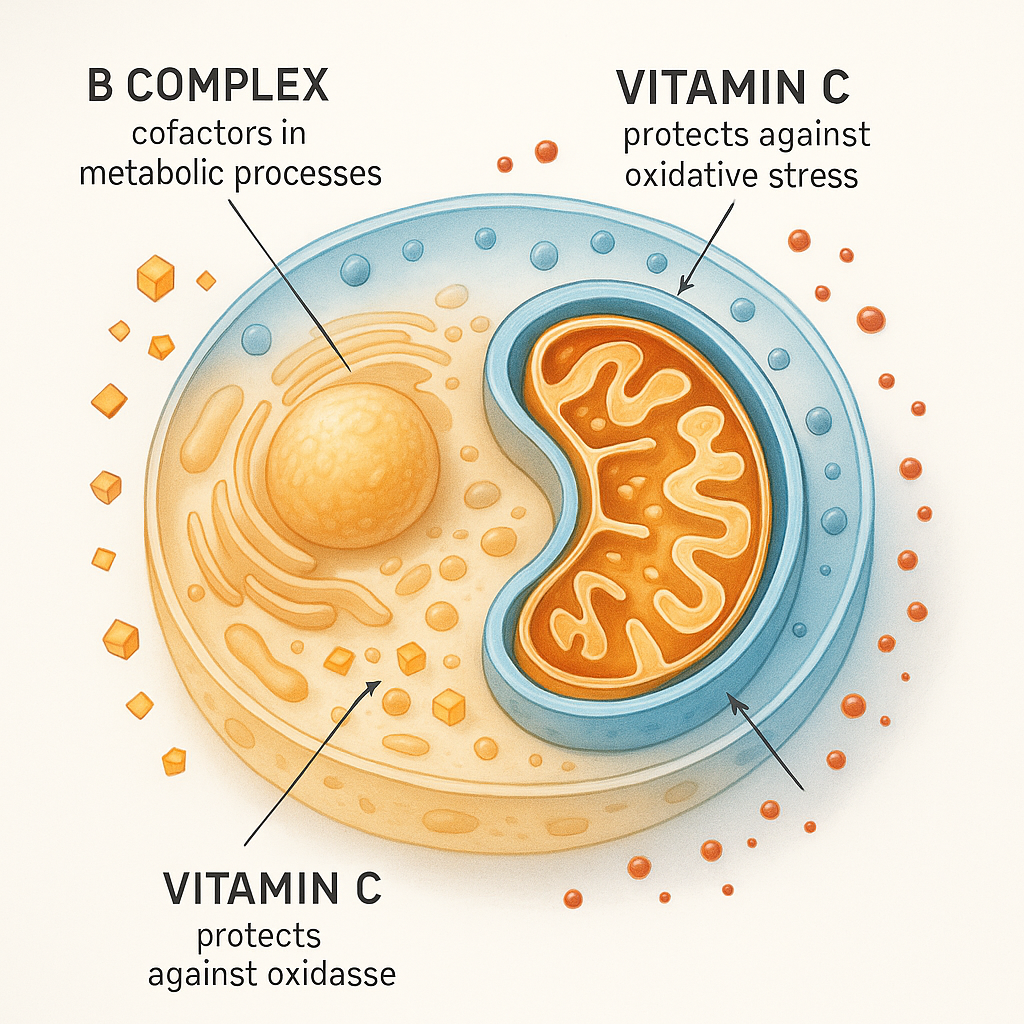
Here’s where natural food sources reveal their advantage. When you consume vitamin C from strawberries or kiwi fruit, you’re delivering the nutrient alongside bioflavonoids like quercetin and hesperidin, compounds that appear to enhance retention and cellular uptake. These plant compounds don’t necessarily increase initial absorption, but they seem to prolong vitamin C activity within tissues and protect it from oxidation. One study examining natural versus synthetic L-ascorbic acid found that while both forms are chemically identical, the presence of these cofactors in natural sources creates measurably different pharmacokinetic profiles.

The daily recommended values tell only part of the story. The RDA for vitamin C ranges from 75mg for adult women to 90mg for men, with increased requirements for smokers, pregnant women, and individuals under physiological stress. Yet many supplements deliver 500mg, 1000mg, or even higher doses—quantities that exceed the body’s absorption capacity and provide diminishing returns beyond satisfying consumer expectations for “more.”
For manufacturers, this absorption science presents a critical formulation challenge: How do you deliver meaningful vitamin C benefits without wasting active ingredients through poor bioavailability? The answer often lies not in higher doses, but in smarter delivery systems and complementary ingredients that mirror the natural complexity of vitamin C foods.
Manufacturing Methods: From Chemical Synthesis to Biotechnology
The journey from glucose to vitamin C supplement reveals manufacturing complexity that directly impacts product quality, sustainability, and market positioning. Understanding these production pathways becomes essential for manufacturers seeking differentiation in an increasingly sophisticated marketplace.
Traditional vitamin C manufacturing relies on the Reichstein process, a chemical synthesis method developed in the 1930s that remains dominant today. This multi-step procedure converts glucose through sorbitol to sorbose, then through protective group chemistry and oxidation to arrive at L-ascorbic acid. The process is remarkably efficient from a cost perspective, yielding pharmaceutical-grade vitamin C at scale. However, it requires significant chemical inputs, generates substantial waste streams, and relies on petroleum-derived solvents—factors increasingly problematic for brands pursuing clean-label positioning.
Modern biotechnology offers compelling alternatives. Two-step fermentation processes employ specific bacterial strains, particularly Gluconobacter oxydans, to convert glucose into 2-keto-L-gulonic acid, which then undergoes simple chemical conversion to ascorbic acid. This biotechnological approach reduces chemical waste, operates at lower temperatures, and aligns more closely with consumer expectations around “natural” production. Several manufacturers have successfully implemented these fermentation methods, though they typically command premium pricing due to higher production costs.
The quality implications between these methods matter less than most marketing claims suggest. Both processes produce chemically identical L-ascorbic acid meeting USP standards. The real differentiation emerges in sustainability profiles, production economics, and marketing narratives. A supplement brand targeting environmentally conscious consumers may justify higher costs through fermentation-based vitamin C, while price-sensitive markets favor traditional synthesis.
Recent innovations explore plant-extraction methods, particularly from fruits exceptionally high in natural vitamin C like camu camu, acerola cherry, and kakadu plum. These extracts deliver vitamin C alongside its natural cofactor matrix, creating products that resonate strongly with whole-food supplement trends. However, standardization challenges, seasonal variability, and significantly higher costs limit their application primarily to premium product lines.
For forward-thinking manufacturers, the choice of vitamin C source becomes a strategic decision balancing cost structures, brand positioning, and target consumer values. Understanding these manufacturing pathways enables more informed sourcing decisions and authentic brand storytelling.
Stability Solutions: Protecting Vitamin C Through Manufacturing and Storage
Vitamin C presents one of the most challenging stability profiles in nutritional manufacturing. Its sensitivity to oxidation, heat, light, and moisture creates formulation obstacles that separate sophisticated manufacturers from those delivering compromised products. The degradation isn’t merely theoretical—poorly stabilized vitamin C supplements lose potency during shelf life, develop off-flavors, and potentially form degradation products that diminish product integrity.
The oxidation pathway represents the primary threat. Vitamin C readily donates electrons, making it an excellent antioxidant but also inherently unstable. When exposed to oxygen, especially in the presence of trace metals or elevated temperatures, ascorbic acid degrades into dehydroascorbic acid and eventually breaks down further into inactive compounds. This degradation accelerates dramatically above pH 4, in aqueous solutions, and under warm storage conditions.
Advanced manufacturers employ several stabilization strategies. Microencapsulation technology coats individual vitamin C particles with protective matrices—typically lipids, proteins, or modified starches—that create physical barriers against oxygen and moisture. These microscopic capsules can improve stability dramatically, with properly designed systems maintaining 95%+ potency over two years compared to 70-80% for unprotected forms. The technology also enables controlled release profiles that can enhance absorption by delivering vitamin C more gradually to intestinal transporters.

Oxygen exclusion during manufacturing and packaging provides another critical control point. Nitrogen flushing during blending, low-oxygen packaging materials, and moisture-barrier bottles all contribute to extended shelf life. Some premium products incorporate oxygen scavengers directly into bottle packaging, actively removing residual oxygen that might degrade vitamin C over time.
Alternative vitamin C forms offer built-in stability advantages. Ascorbyl palmitate, a fat-soluble vitamin C ester, demonstrates markedly improved stability compared to pure ascorbic acid. Mineral ascorbates like sodium ascorbate or calcium ascorbate buffer the pH, reducing acid-catalyzed degradation. These derivatives require enzymatic conversion in the body to release active vitamin C, but their enhanced stability makes them valuable for certain applications.
At NutraAeon, we recognize that stability isn’t just a technical specification—it’s a promise to consumers that the product they purchase delivers its claimed benefits throughout shelf life. Our comprehensive testing protocols monitor stability under accelerated conditions, ensuring that sourced ingredients meet rigorous quality standards from manufacturing through expiration. This commitment to quality and transparency allows our manufacturing partners to formulate with confidence, knowing their vitamin C ingredients will perform as expected.
Consumer-Facing Implications: Taste, Perception, and Clean-Label Demands
The technical excellence of vitamin C manufacturing means little if consumers reject products based on sensory experience or perceive them as inconsistent with their values. Today’s health-conscious consumers approach supplements with sophisticated expectations around taste, ingredient transparency, and the natural-versus-synthetic debate that shapes purchasing decisions across the nutritional products industry.
Taste presents an immediate challenge. Pure ascorbic acid delivers pronounced sourness that many consumers find unpleasant, particularly in chewable formats or drink mixes. This acidity isn’t merely an aesthetic concern—it can irritate sensitive stomachs and contribute to dental enamel erosion with frequent use. Manufacturers address these issues through various approaches: buffered forms that neutralize acidity, flavor masking systems, or reformulation into capsules that bypass taste entirely. Each solution carries trade-offs in cost, consumer preference, and formulation complexity.
The natural versus synthetic debate generates passionate consumer opinions often disconnected from scientific reality. While chemically identical L-ascorbic acid from synthesis and whole food sources behave identically at the molecular level, consumer perception differs dramatically. Marketing research consistently shows that significant consumer segments willingly pay premium prices for “natural” vitamin C, even when bioavailability data shows no meaningful advantage. This perception gap creates both opportunities and ethical considerations for manufacturers.
Clean-label trends fundamentally reshape ingredient selection criteria. Consumers increasingly scrutinize ingredient lists, favoring recognizable names over chemical terminology. “Ascorbic acid” faces more skepticism than “vitamin C from acerola cherry,” regardless of functional equivalence. This shift drives growing demand for whole-food vitamin C sources, plant-based capsules, and formulations free from synthetic additives, colors, or preservatives.
Forward-thinking manufacturers recognize these consumer preferences as formulation requirements rather than obstacles. They develop products that deliver technical efficacy while respecting consumer values around ingredient transparency. This might mean choosing more expensive natural vitamin C sources for premium lines while maintaining synthetic options for price-sensitive markets—a portfolio approach that serves diverse consumer segments authentically.
The key lies in honest communication. Manufacturers who clearly explain their ingredient choices, acknowledge both natural and synthetic forms as legitimate options, and focus on delivering measurable benefits build stronger consumer trust than those making exaggerated naturalness claims. NutraAeon supports this philosophy by empowering our manufacturing partners with complete ingredient documentation, transparent sourcing information, and technical expertise that enables informed formulation decisions aligned with brand values.
Regulatory Considerations and the Importance of Accurate Labeling
Vitamin C’s regulatory landscape demands careful navigation as manufacturers balance marketing aspirations with compliance requirements. The FDA regulates vitamin C as both a dietary supplement and a food additive, with distinct rules governing claims, labeling, and quality standards that shape how products reach consumers.
Dietary supplement manufacturers must adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) that mandate identity testing, potency verification, and purity analysis for every vitamin C ingredient. These regulations require documented testing proving that products contain what labels claim within specified tolerances—typically 100-150% of labeled amounts for vitamins to account for degradation during shelf life. Manufacturers who cut corners on testing or overstate potency face regulatory action and consumer trust erosion.
Label claims present particularly complex terrain. While manufacturers may state that vitamin C “supports immune function” or “provides antioxidant support,” disease treatment claims remain prohibited without FDA approval as a drug. The line between permissible structure-function claims and illegal disease claims often appears subtle but carries significant legal consequences. Phrases like “boosts immunity” must become “supports immune health,” while any mention of treating or preventing specific diseases triggers immediate regulatory concerns.
The natural versus synthetic designation carries specific regulatory implications. Products labeled “natural vitamin C” must derive from whole food sources, not synthetic ascorbic acid. The term “natural flavors” has defined regulatory meaning distinct from casual marketing usage. Manufacturers making “organic” claims must comply with USDA organic certification requirements. These distinctions matter because regulatory agencies and consumers increasingly scrutinize naturalness claims that lack substantiation.
Certificate of Analysis documentation becomes essential for regulatory compliance and supply chain transparency. Quality manufacturers provide comprehensive COAs showing vitamin C potency, heavy metal testing, microbiological analysis, and verification of identity through multiple analytical methods. These documents create accountability and traceability from raw material through finished product—protection against contamination, adulteration, or quality failures that could jeopardize brand reputation.
NutraAeon’s dedication to providing full supply chain visibility directly addresses these regulatory complexities. We work with manufacturing partners to ensure complete documentation, accurate certificates of analysis, and regulatory guidance that supports compliant product development. Our rigorous quality standards exceed basic FDA expectations, incorporating USP monograph specifications and additional testing protocols that provide confidence throughout the product lifecycle. This comprehensive approach empowers manufacturers to navigate regulatory requirements while focusing on innovation and market growth.
Partnering for Innovation: NutraAeon’s Vision for Vitamin C Excellence
The vitamin C manufacturing landscape reveals complexity that demands expertise, quality commitment, and strategic partnership rather than transactional ingredient purchasing. Successful supplement brands recognize that ingredient sourcing represents a critical competitive advantage—one that requires partners who understand technical nuances, regulatory requirements, and market dynamics shaping the nutritional products industry.
NutraAeon’s vision centers on being that premier global sourcing partner, connecting forward-thinking manufacturers with nutritional ingredients that enable market-leading products. Our vitamin C portfolio spans multiple forms—from pharmaceutical-grade ascorbic acid to fat-soluble ascorbyl palmitate to buffered mineral ascorbates—each selected for specific application advantages and backed by comprehensive quality documentation. This diversity allows our partners to optimize formulations for target markets, whether premium natural products or cost-effective mass-market supplements.
Beyond ingredient supply, we provide the technical expertise that transforms raw materials into successful products. Our team offers formulation guidance addressing stability challenges, bioavailability optimization, and sensory considerations that determine market acceptance. We understand that vitamin C rarely functions alone—it works synergistically with vitamin E, bioflavonoids, and other nutrients—so we support holistic formulation strategies that deliver superior consumer outcomes.
Market insights distinguish strategic partners from commodity suppliers. We monitor emerging trends, regulatory developments, and consumer preference shifts that shape product innovation opportunities. Whether it’s growing demand for liposomal delivery systems, interest in fermentation-derived ingredients, or clean-label reformulation requirements, we help manufacturers stay ahead of market evolution rather than reacting to it.
Our commitment to excellence manifests through industry-leading testing protocols and quality standards that exceed compliance baselines. Every vitamin C ingredient undergoes rigorous identity verification, potency analysis, heavy metal screening, and microbiological testing before reaching our partners. This quality assurance creates the foundation for products that perform consistently, satisfy regulatory requirements, and build lasting consumer trust.
For manufacturers seeking to innovate with confidence, NutraAeon offers more than ingredients—we provide partnership. Our scientific expertise, market insights, and dedication to transparency empower brands to create nutritional products that stand out in competitive landscapes. Whether you’re developing premium vitamin C supplements that mirror whole food complexity or formulating cost-effective products for mass markets, our comprehensive support ensures your formulations achieve both technical excellence and commercial success.
The secret that vitamin C foods reveal isn’t just about cofactors and bioavailability—it’s about understanding nutrition’s complexity and approaching manufacturing with the respect that complexity deserves. By partnering with sources committed to quality, transparency, and empowerment, manufacturers can create vitamin C products that truly deliver the benefits consumers seek. That’s the NutraAeon difference, and the foundation for nutritional innovation that makes a meaningful difference in people’s lives.